backup [--full] [filename] -- Stores the current configuration of openHAB.
clean-cache -- Cleans the openHAB temporary folders.
console -- Opens the openHAB console.
info -- Displays distribution information.
reset-ownership -- Gives openHAB control of its own directories.
restore [--textconfig] [--uiconfig] filename
-- Restores openHAB configuration from a backup.
showlogs -- Displays the log messages of openHAB.
start [--debug] -- Starts openHAB in the terminal.
status -- Checks to see if openHAB is running.
stop -- Stops any running instance of openHAB.Category Archives: IT
Command a Philips Hue light from a KNX switch through openHAB
I am using openHAB as my main home automation server. I want to be able to switch on/off Philips Hue lights with the Gira KNX TS3 sensors installed in my rooms.
Basically, you need to create a group address, map it to the TS switch channel, create a virtual KNX device in openHAB and create two rules to link both objects (one rule for switching ON and one for switching OFF).
In the ETS software, create a group address (e.g. 1/9/9) and map it to the TS button’s channel that should allow switching the Hue light ON and OFF.
In openHAB, create a KNX device thing called Virtual KNX switch. Add a channel with type Switch Control and configure it to address 1/9/9. Map an item of type Contact to this channel (let’s name it KitchenVirtualSwitch).
Assuming that your Hue light is called HueLight, create a rule to switch the light ON:
configuration: {}
triggers:
- id: "1"
configuration:
command: ON
itemName: KitchenVirtualSwitch
type: core.ItemCommandTrigger
conditions: []
actions:
- inputs: {}
id: "2"
configuration:
type: application/vnd.openhab.dsl.rule
script: "
\ HueLight.sendCommand(ON)
\ logInfo( \"openHAB.Rules\",\"KitchenVirtualSwitch TS => Hue ON\"
)
\ "
type: script.ScriptActionThe logInfo entry is optional, but very helpful when debugging. Let’s create a second rule for switching the light OFF:
configuration: {}
triggers:
- id: "1"
configuration:
command: OFF
itemName: KitchenVirtualSwitch
type: core.ItemCommandTrigger
conditions: []
actions:
- inputs: {}
id: "2"
configuration:
type: application/vnd.openhab.dsl.rule
script: "
\ HueLight.sendCommand(OFF)
\ logInfo( \"openHAB.Rules\",\"KitchenVirtualSwitch TS => Hue OFF\"
)
\ "
type: script.ScriptAction
Home Assistant Nginx Proxy configuration
Here is a working NGINX proxy configuration for Home Assistant:
server {
server_name HOST.DOMAIN.NAME;
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
location / {
satisfy any;
allow 10.X.X.0/24;
allow 10.X.X.0/24;
deny all;
auth_basic "Restricted access";
auth_basic_user_file /etc/passwords/passwords;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_headers_hash_max_size 512;
proxy_headers_hash_bucket_size 128;
proxy_pass http://INTERNAL_HOME_ASSISTANT_IP:8123;
include proxy_params;
}
listen 443 ssl;
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/HOST.DOMAIN.NAME/fullchain.pem; # managed by Certbot
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/HOST.DOMAIN.NAME/privkey.pem; # managed by Certbot
}
server {
if ($host = HOST.DOMAIN.NAME) {
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
} # managed by Certbot
listen 80;
server_name HOST.DOMAIN.NAME;
}openHAB delete stubborn things
If you try to delete a thing via the GUI in openHAB 4 and it does not get removed (status remains stuck on: removing), you can remove it using the CLI.
For this, login to the karaf console:
openhab-cli consoleUsername: openhab ; password: habopen
openhab:things remove thing:full:nameInstall Cockpit management on Ubuntu
If you want to install cockpit on your server, follow these steps:
To install cockpit on Ubuntu, run the following command:
sudo apt install cockpitAdditionally, install the following package for more detailed metrics:
sudo apt install cockpit-pcpNow there is a bug in Ubuntu, prohibiting cockpit to update the system through the webinterface (packagekit cannot refresh cache whilst offline). This seems to have to do with differences in netplan and network manager. To overcome this, you have to create a a placeholder file and a network interface:
nano /etc/NetworkManager/conf.d/10-globally-managed-devices.confAdd the following two lines to that file. Save the file ant quit the nano editor.
[keyfile]
unmanaged-devices=noneOptionally: If you run Ubuntu on an ARM system, you may need to install the following packages:
sudo apt install linux-modules-extra-raspiNow set up a dummy network interface:
nmcli con add type dummy con-name fake ifname fake0 ip4 1.2.3.4/24 gw4 1.2.3.1Reboot your machine. Now you should be able to update the packages in the web interface.
Cockpit should be starting automatically. If this does not happen, configure it to do so:
systemctl start cockpit
systemctl enable cockpitAccess your cockpit installion under https://my.server.IP.address:9090
Source: https://cockpit-project.org/faq.html
Auto start issues?
If you happen to see the following error when enabling cockpit:
The unit files have no installation config (WantedBy=, RequiredBy=, Also=, Alias= settings in the [Install] section, and DefaultInstance= for template units). This means they are not meant to be enabled using systemctl.Than you have to edit the configuration file:
sudo nano /usr/lib/systemd/system/cockpit.serviceAnd add the following lines at the end, save and start the service:
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetsystemctl enable cockpit.service
systemctl start cockpit.serviceMake new disk usable in Linux
After installing a new hard drive, you have to follow a few steps to make it usable on your Linux system. Be sure not to erase an existing file system.
- (1) Identify the disk “fdisk -l“
fdisk -l- (2) Partition the disk with fdisk or cfdisk
cfdisk /dev/sdX- (3) Create the filesystem (format the disk) on each created partition. To create an ext4 filesystem on partition /dev/sdXY run:
mkfs.ext /dev/sdXY- (4) Define the mount point for the newly created filesystem editing fstab:
nano /etc/fstabAdd the line for the newly created filesystem. I prefer to refer to it by UUID and not by device ID (these might change). Get the ID using this command “cd /dev/disk/by-uuid” and “ls -l”.
/dev/disk/by-uuid/3a9128c0-c9c2-47e7-b9f0-edc049ff4d3f /data ext4 defaults 0 1source: https://superuser.com/questions/872257/how-to-make-a-new-disk-usable-on-ubuntu-linux
Change home directory on Linux
usermod -d /new/homedirectory usernameUsing ACL permissions in Ubuntu
List ACL’s for a given directory
getfacl /var/www# file: www
# owner: root
# group: root
user::rwx
group::r-x
other::r-xYou might need to install ACL (apt install acl).
Add a group to an ACL
Use setfacl to add a group to the ACL
setfacl -m g:family:rwx /var/www/This leads your check on ACL like this:
# file: www
# owner: root
# group: root
user::rwx
group::r-x
group:family:rwx
mask::rwx
other::r-xRemoving an ACL entry:
setfacl -x g:family /var/wwwGranting an additional user read-write access
setfacl -m u:jhemp:rw /var/wwwMore information: https://help.ubuntu.com/community/FilePermissionsACLs
Synchronise two Pi-hole servers
If you run more than one Pi-hole server in your network, it can be handy to synchronise both instances so that you do not need to add and maintain your local DNS entries and your ad-block lists on two different machines.
Currently you have two possibilities do achieve this: Orbital-sync and Gravity-sync. Orbital-sync uses the admin interfaces to synchronise. Gravity-sync connects both instances via SSH.
To set up gravity-Sync, you have to do the following:
- As a precaution, backup both instances of Pi-hole using the backup function (under Settings, Teleporter tab) and, if you use a virtualisation environment, take snapshots of both instances.
- If the two Pi-hole servers are running in different VLAN’s, do not forget to set up the corresponding firewall rules (for both directions).
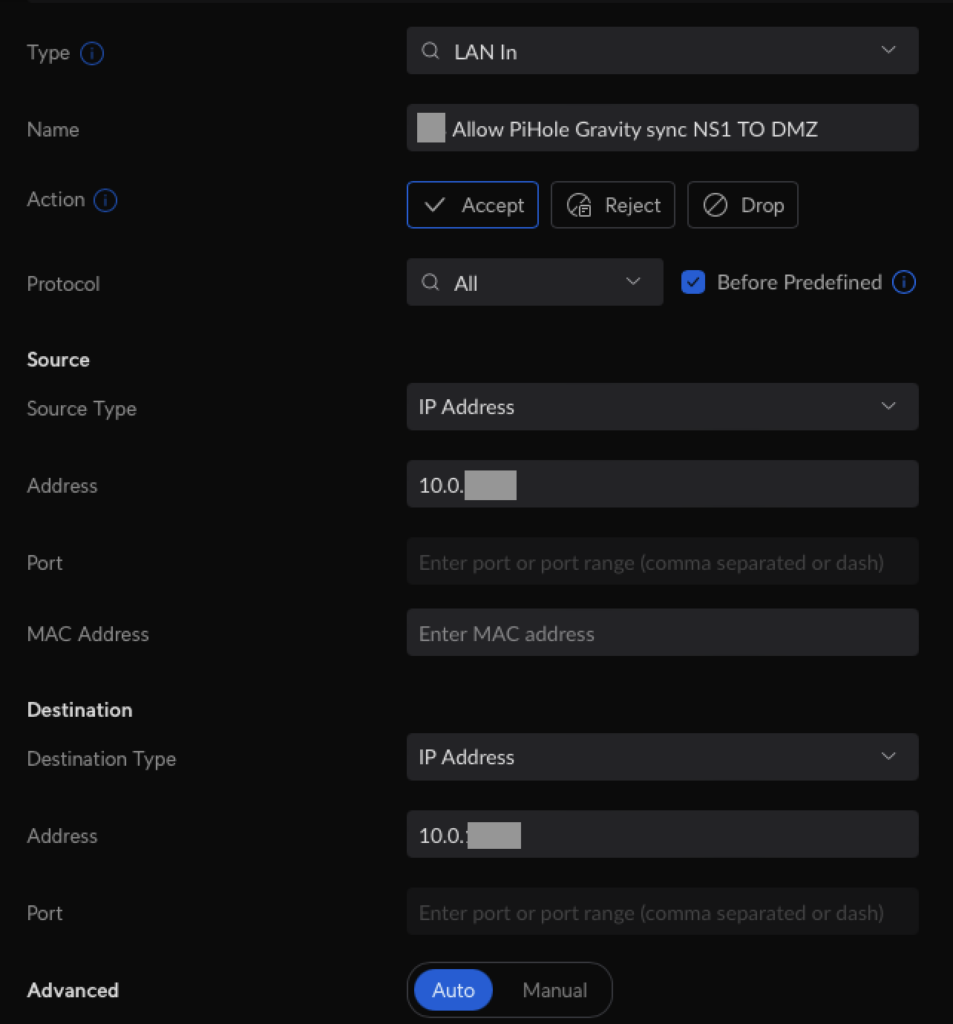
- On both Pi-hole instances: Install Gravity-sync using this command (source):
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/vmstan/gs-install/main/gs-install.sh | bashA wizard will ask you for the connection information (IP, user, password) for the remote host. The configuration will be saved in /etc/gravity-sync/gravity-sync.conf.
- On both Pi-hole instances: Run a comparison of the local and remote Pi-hole databases using:
gravity-sync compare- On your master Pi-hole instance, push the configuration from your master to the slave instance. Be careful not to push a default or incomplete configuration of a new instance to your running instance.
gravity-sync push- On both Pi-hole instance: To automate synchronisation run the following command:
gravity-sync auto- Additionally: to adjust the frequency of updating, run one of the following commands:
gravity-sync auto hour
gravity-sync auto half
gravity-sync auto quadEnable root user to login via SSH
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_configUncomment the following entry in the sshd configuration file and change it to yes:
PermitRootLogin YesRestart the SSH service
sudo systemctl restart sshdYou have to create a password for the root user:
sudo passwd root